Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Suzuki, Takashi; Tanaka, Takayuki
KURRI-KR-153, p.41 - 46, 2010/03
It is considered that recent distribution of anthropogenic radionuclides in the Japan Sea was controlled by supply of the radionuclides due to the global fallout and seawater circulation of the interior of the sea, rather than by a specific nuclear facility/incident. The detailed transport processes, however, have not been elucidated at the present. In this study, the authors surveyed distribution of radiocarbon at 81 stations in the Japan Sea and traced the fate of anthropogenic radiocarbon. As a result, principal transport process of radiocarbon, such as (1) supply from the East China Sea, (2) northward transport at the surface according to the Tsushima Warm Current, and (3) vertical transport in the northwestern region, were confirmed. In addition, the amount of anthropogenic radiocarbon in the sea was estimated by using a simple box-model.
 C measurement at JAEA-AMS-MUTSU
C measurement at JAEA-AMS-MUTSUTanaka, Takayuki; Kabuto, Shoji; Kinoshita, Naoki; Yamamoto, Nobuo
KURRI-KR-153, p.29 - 34, 2010/03
An accelerator mass spectrometry at Mutsu office, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA AMS MUTSU) was established in 1997 and the routine operation of radiocarbon measurement was started from 1999. The radiocarbon was measured by 1,193 samples last year, and the number of radiocarbon measurements reached 8,809 samples since the routine operation. This AMS has adopted the open door policy for the general users from the fiscal year of 2006 and various researches have been in progress by many users. As a operate system of this AMS had been controlled under Windows 3.1 since installation, it was difficult to purchase spare parts which are compatible with Windows 3.1. The operation system was upgraded to Windows XP in this year. In this presentation, I introduce the current status of JAEA AMS MUTSU, upgrading of the operation system and moreover an extraction method for determination of dissolved organic radiocarbon which was developed in this year.
 C to study soil carbon cycling in beech forest
C to study soil carbon cycling in beech forestAtarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Koarashi, Jun; Ishizuka, Shigehiro*; Hirai, Keizo*
KURRI-KR-153, p.8 - 13, 2010/03
Soil organic carbon (SOC) is a complex of materials with different ages. An understanding of soil carbon cycling and thereby predicting its response to climatic change requires knowledge of both the inventory of carbon and the turnover times of SOC. In this study, chemical and density fractionation were examined to separate the organic matter collected from a beech forest into components with different turnover times. Mean residence time (MRT) for each fraction was estimated from its radiocarbon isotope ratio (
 C) using the
C) using the 
 C-MRT model. The results show that fractions separated by chemical fractionation with acid-alkali treatment have clearer difference in the isotope ratio than that by density fractionation. This means chemical fractionation is more adequate to estimate MRT composition for the beech forest soil. We also observed differences in the inventory and MRTs of carbon using chemical fractionation for two forests with different vegetation and the mean temperature. The results show that the difference in decomposed carbon flux from these two forests is attributed to the difference in MRT composition in each forest.
C-MRT model. The results show that fractions separated by chemical fractionation with acid-alkali treatment have clearer difference in the isotope ratio than that by density fractionation. This means chemical fractionation is more adequate to estimate MRT composition for the beech forest soil. We also observed differences in the inventory and MRTs of carbon using chemical fractionation for two forests with different vegetation and the mean temperature. The results show that the difference in decomposed carbon flux from these two forests is attributed to the difference in MRT composition in each forest.
 derived from soil organic matter decomposition over the incubation time
derived from soil organic matter decomposition over the incubation timeMoriya, Koichi*; Moriizumi, Jun*; Yamazawa, Hiromi*; Koarashi, Jun; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko
KURRI-KR-153, p.53 - 59, 2010/03
To understand the decomposition mechanism in the soil, we researched the relationship between compositions of SOM and CO derived from SOM decomposition (SOMD-CO
derived from SOM decomposition (SOMD-CO ) by using
) by using  C and
C and  C. With the soil incubation, we measured CO
C. With the soil incubation, we measured CO production rates of soil and carbon isotopic ratios in SOMD-CO
production rates of soil and carbon isotopic ratios in SOMD-CO . The CO
. The CO production rates decreased rapidly at the beginning of incubation, and then decreased slowly. On the other hand,
production rates decreased rapidly at the beginning of incubation, and then decreased slowly. On the other hand, 
 C
C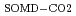 before incubation was larger than
before incubation was larger than 
 C
C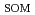 . After 40-70 days of incubation,
. After 40-70 days of incubation, 
 C
C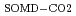 became smaller than
became smaller than 
 C
C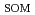 , and then
, and then 
 C
C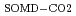 after 120-170 days approached
after 120-170 days approached 
 C
C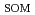 . We consider these results as follows. SOM is composed of three components, rapidly decomposable SOM that has large
. We consider these results as follows. SOM is composed of three components, rapidly decomposable SOM that has large 
 C, slowly decomposable SOM that has small
C, slowly decomposable SOM that has small 
 C and passive SOM that has the same value as
C and passive SOM that has the same value as 
 C
C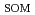 . With the progress of soil decomposition, the dominant component in SOMD-CO
. With the progress of soil decomposition, the dominant component in SOMD-CO changed. Therefore,
changed. Therefore, 
 C
C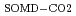 changed too.
changed too.